You are here
Tannery Effluent Treatment
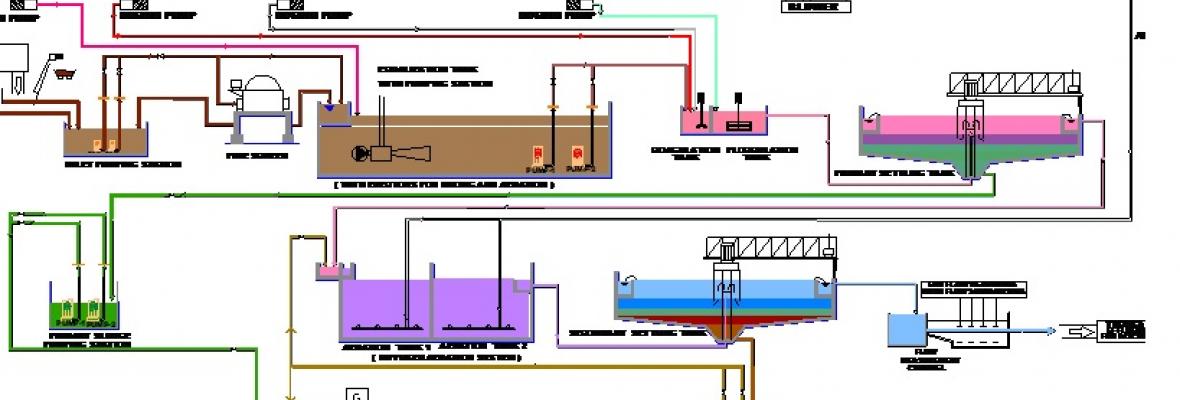
Despite all preventive measures, a sizeable portion of pollutants can only be removed by the end-of-pipe methods, i.e. treating effluents discharged in the course of leather processing. One of the most successful areas of interventions implemented or facilitated by UNIDO was designing and managing the construction of cost effective [Common] Effluent Treatment Plants ([C]ETP). More than 250 such plants have been designed, established or upgraded through various technical assistance projects. Achievements and experiences were documented in technical papers, reports and manuals which are available in this section. A special Animated Visual Training Tool was also developed by UNIDO and is available in the section “e-Learning".